A Comprehensive Guide to Solar Home Systems
Release Time:
2023-05-09
As the world continues to move toward clean and renewable energy sources, solar home systems have gained immense popularity for their ability to provide sustainable and cost-effective electricity. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of solar home systems, their components, categories, and applications. Let's delve deeper into the world of solar home systems and learn how they can power your home while reducing your carbon footprint.
Section 1: What is a Solar Home System?
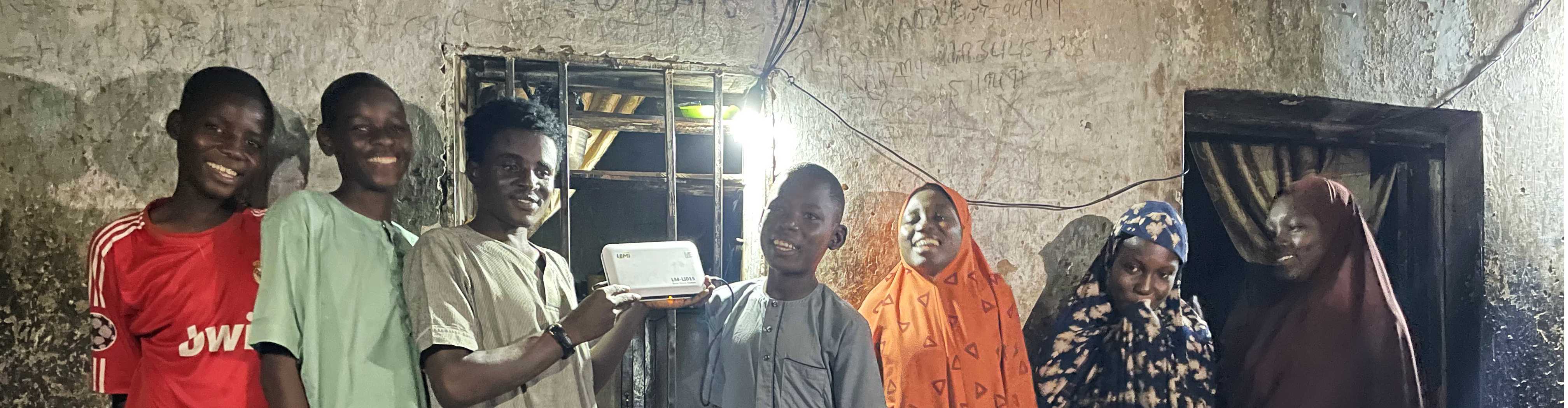
A solar home system is a stand-alone, decentralized power generating system that harnesses sunlight to produce electricity for residential use. It typically includes solar panels, a charge controller, a battery bank, and in certain cases, an inverter, which work together to convert sunlight into usable power for your home appliances and electronics. By using a solar home system, people living in off-grid area with no access to electricity can be empowered by solar energy and properly conduct daily activities. Homeowners can reduce or eliminate their reliance on grid electricity, thereby lowering their energy bills and reducing their carbon emissions.
Section 2: Components of a Solar Home System
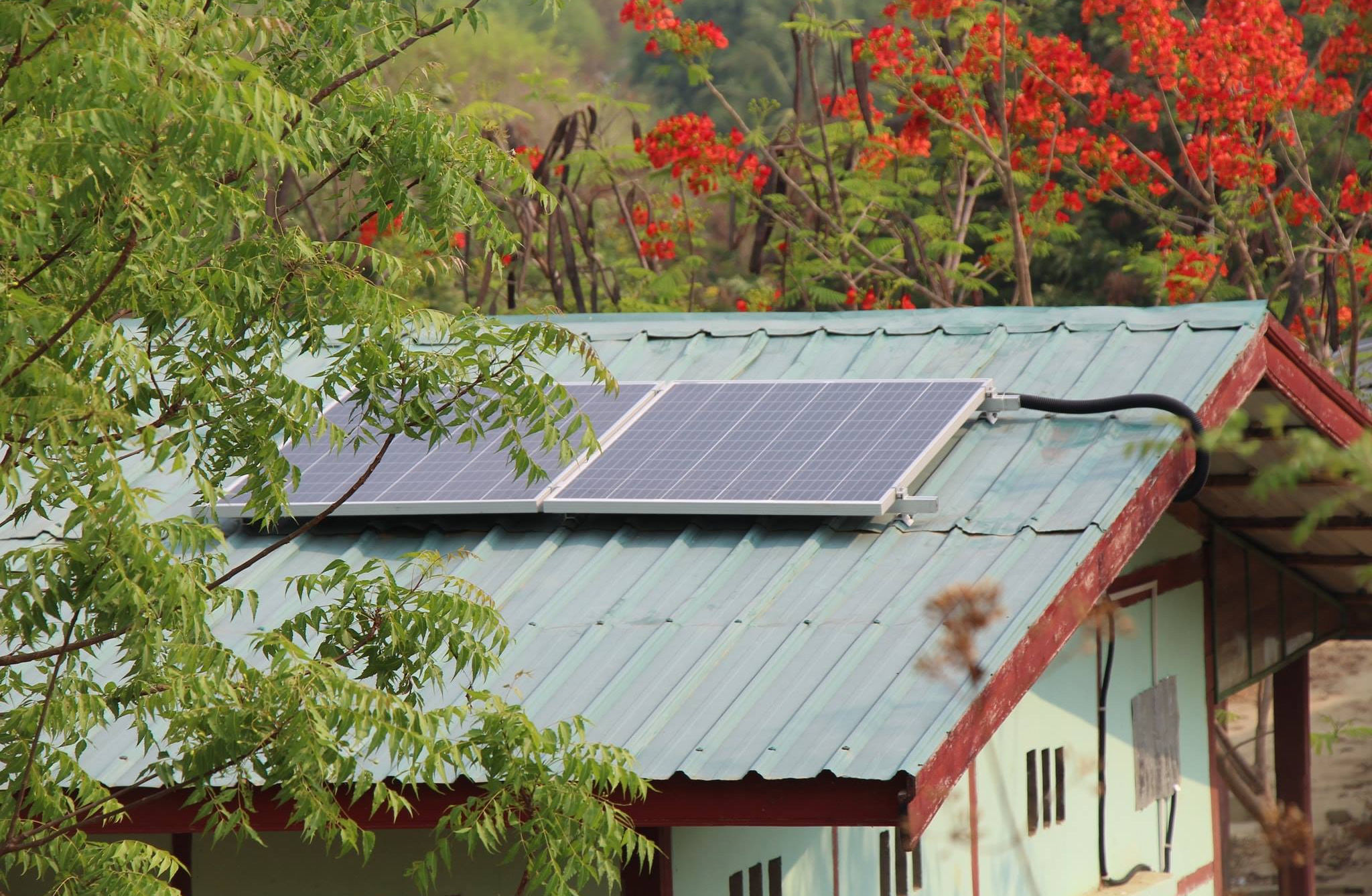
- Solar Panels: Solar panels, or photovoltaic (PV) modules, are the primary components that convert sunlight into electricity. They are made of silicon cells, which absorb sunlight and generate a flow of electrons, creating a direct current (DC).
- Charge Controller: The charge controller regulates the flow of electricity between the solar panels and the battery bank. It ensures that the batteries are charged efficiently and prevents them from overcharging or discharging too rapidly. In certain products, the controller can also discharge direct current (DC) from the battery and power appliances directly.
- Battery Bank: The battery bank stores the electricity generated by the solar panels. This stored energy can be used during periods of low sunlight or at night when the solar panels are not producing power.
- Inverter: The inverter converts the DC electricity generated by the solar panels and stored in the battery bank into alternating current (AC), which is the type of electricity used by most household appliances and electronics.
Section 3: Categories of Solar Home Systems
Solar home systems can be broadly categorized into two types based on their connection to the grid:
- Off-grid Solar Home Systems: These systems operate independently of the grid and solely rely on solar power and battery storage for electricity. They are ideal for remote locations where grid access is limited or unavailable.
- Grid-tied Solar Home Systems: These systems are connected to the grid and use solar power in conjunction with grid electricity. When solar production exceeds a home's energy needs, excess electricity can be fed back into the grid, often generating credits on the homeowner's utility bill.
Section 4: Applications of Solar Home Systems
- Lighting: Solar home systems can provide power for indoor and outdoor lighting, reducing the need for grid-supplied electricity or as the lighting solution at off-grid area.
- Appliances: Solar home systems can power a wide range of appliances, including television, fan, refrigerators, washing machines, and air conditioners, making them more energy-efficient and eco-friendly.
- Electronics: Solar-generated electricity can be used to charge laptops, smartphones, and other electronic devices.
- Water Heating: Solar home systems can be integrated with solar water heaters, providing an energy-efficient way to heat water for domestic use.
- Backup Power: Solar home systems can serve as a reliable backup power source during power outages, ensuring uninterrupted access to electricity.
Conclusion:
Solar home systems offer a clean, renewable, and cost-effective alternative to traditional grid electricity. By understanding their components, categories, and applications, homeowners can make informed decisions about implementing solar home systems to power their homes and contribute to a more sustainable future. Investing in a solar home system is not only a step towards energy independence but also a commitment to protecting our environment for generations to come.
Recommend
Want to learn more or ask for help?